Home Case Studies SCATTER Emissions Reporting Tool for Local Authorities
SCATTER Emissions Reporting Tool for Local Authorities

Home Case Studies SCATTER Emissions Reporting Tool for Local Authorities

The launch of SCATTER follows the UK government’s climate emergency declaration in 2019. Since then, hundreds local authorities across the UK have also made similar declarations and commitments.
A user-friendly interactive greenhouse gas reporting tool that helps local authorities to assess, report on and reduce the amount of greenhouse gas emissions that their area produces.
The climate crisis has prompted numerous local authorities across the UK to make declarations and commitments around climate action and sustainability. As these authorities continue to seek effective strategies to reduce carbon emissions, a challenge has arisen around understanding, measuring, and reporting area-wide greenhouse gas emissions accurately. With many cities pledging significant carbon reduction goals, the need for a comprehensive tool to assess, report, and reduce emissions has become crucial.
Anthesis, in collaboration with Nottingham City Council, BEIS, Greater Manchester Combined Authority, and the Tyndall Centre for Climate Research at the University of Manchester, developed SCATTER (Setting City Area Targets and Trajectories for Emissions Reduction). SCATTER is a user-friendly, web-based, interactive greenhouse gas reporting tool designed to assist local authorities. It uses various national and local public datasets to quantify outputs without requiring significant resource commitments from local authorities. The tool integrates key technologies such as carbon capture, decarbonising heat, energy efficiency, electrifying transport, and recycling infrastructure improvements.
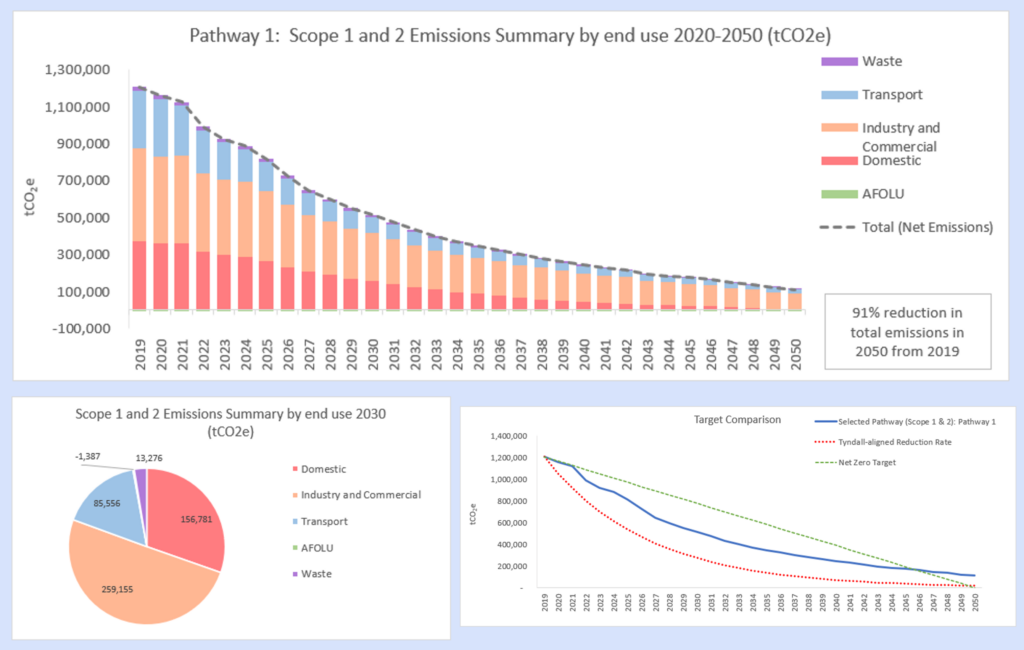
SCATTER has been adopted by more than 320 local authorities in the UK, with 41 out of 60 UK cities disclosing their emissions using the tool. SCATTER enables local authorities to build detailed inventories of their area’s annual greenhouse gas emissions, identify major emission sources, and model scenarios for reduction. The “Pathways” feature allows authorities to explore different greenhouse gas reduction actions and create scenarios for emissions reduction pathways to 2050.
The tool has facilitated effective stakeholder engagement, as evidenced in its use by sector leads in commercial organisations, housing associations, transport, energy distributors, technology providers, and academic institutions. Local authorities using SCATTER have gained valuable insights, improved transparency, and can now actively contribute to national and international climate change objectives, including initiatives such as the UK’s 2050 Net Zero target and the Paris Agreement.
SCATTER can be used to obtain the data for carbon disclosure, such as Climate reporting NGO CDP, where companies, cities and regions submit data on their environmental performance. By disclosing to initiatives like CDP, local authorities can better understand the scale of their impact on carbon reduction, as well as ways they can support crucial initiatives such as the UK’s 2050 Net Zero target and international Paris Agreement.
Reporting into the CDP-ICLEI Unified System gives local authorities data-driven insights into their climate action. It allows local authorities to transparently track their progress, access best practice and share their data with networks like the Global Covenant of Mayors.
The Environmental Insights Explorer (EIE) from Google puts the Anthesis-developed SCATTER tool in the spotlight.
The Google Environmental Insights Explorer tool, created in partnership with the Global Covenant of Mayors for Climate & Energy, has been designed to give cities and local governments access to their current emission levels, so they can build a plan to reduce and measure emission levels.
Using data from Google Maps alongside standard greenhouse gas (GHG) emission factors, EIE estimates three city-level data points: building emissions, transport emissions and renewable energy potential (solar).
The tool highlights the significant scale of city emissions and with it their role in being part of the solution. Using common methodology that can be standardised and scaled, it makes it easy for cities to benchmark their emissions against other cities. The tool will be used by city policymakers to develop clear plans of action to reduce their carbon emissions.
The SCATTER carbon footprint tool builds upon similar details provided by the EIE to allow cities to drill into the interventions; the areas of activity where the potential for carbon reduction lies.
Whereas Google looks at three main interventions (buildings, transportation and solar), SCATTER focuses on a comprehensive list of 45 interventions. Google helps to identify the scale of the problem, while SCATTER enables cities and regions to develop a picture of the solution by building up future reduction scenarios from detailed practical from detailed practical areas under a city’s control.
This supports local climate action planning and responses to the climate emergency, as well as allowing cities and governments to get an accurate handle of their current emissions and set carbon reduction trajectories and targets that are driven by a technology led approach. This leads to evidence based targeting setting and informed policy making.
Not only is SCATTER supporting CDP submissions, it also has a range of standard outputs that can translated using the latest data visualisation software to support messaging and make it simple for policymakers and planners to explore future carbon reduction scenarios. Robust datasets are only as good as the user’s ability to interpret it, so ‘seeing’ the outcome of the policy decisions they may or may not decide to make is a crucial to simplifying complex data.
For example, a city could model the impact of improving energy efficiency in buildings via retrofit scenarios and new technologies to reduce heat leakage. Or a city could track how carbon capture storage will reduce emissions from industrial use and power generation before investing. Being able to see the potential impacts is a huge benefit for decision makers.
Local authorities can use SCATTER to build a detailed inventory of their area’s annual greenhouse gas emissions in order to identify their largest emissions sources.
In addition, a new feature called “Pathways” allows local authorities to explore different greenhouse gas reduction actions and enable the creation of reduction scenarios from which to develop their climate action plans for their area to 2050.
Pathways allow SCATTER users to select the level of ambition for a range of interventions and model different scenarios for their emissions reduction pathway to 2050.
Within each city-region, we’re also working with sector leads using the SCATTER tool as an effective and dynamic stakeholder engagement vehicle. We’ve spoken to leaders in commercial organisations, housing associations and domestic, transport, energy distributors, technology providers and academic institutions.
SCATTER is a collaboration between Anthesis Group, Nottingham City Council, BEIS, Greater Manchester Combined Authority and the Tyndall Centre for Climate Research at the University of Manchester.